[最も欲しかった] p(x y) joint probability density function 442894-What is joint probability density function
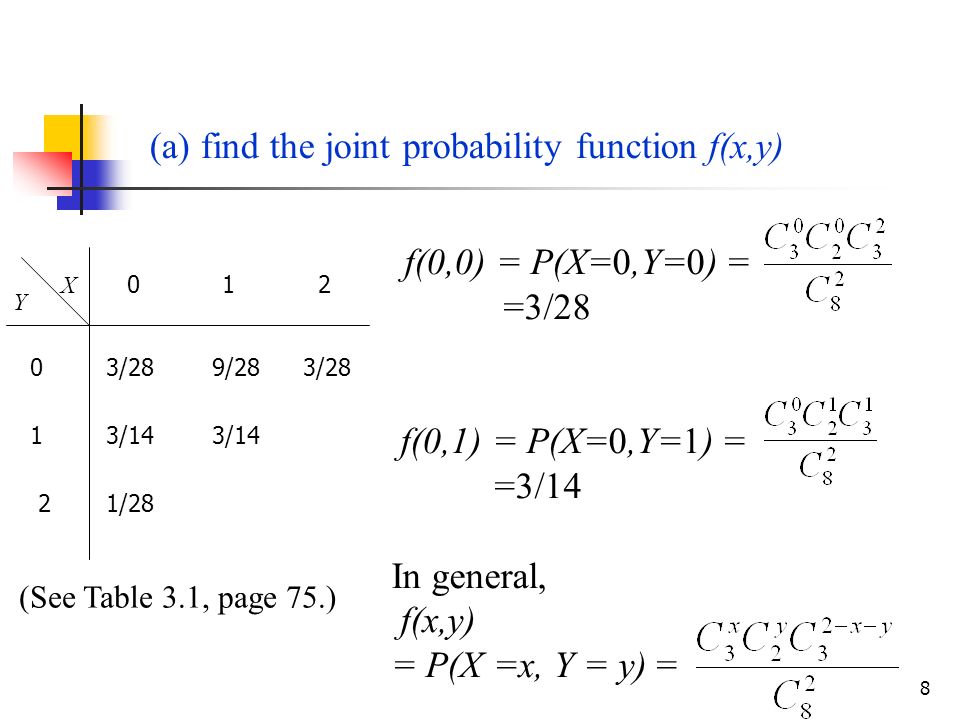
12 (10 points) Let X and Y have joint probability density function defined by f (X,Y) (x, y) = 1 2 x, if 0 < y < x < 2;• The probability of event {(X,Y)∈ B} is P(B)= X (x,y)∈B PX,Y (x,y) – Two coins, one fair, the other twoheaded A randomly chooses one and B takes the other X = ˆ 1 A gets head 0 A gets tail Y = ˆ 1 B gets head 0 B gets tail Find P(X ≥ Y) • Marginal probability mass function of X can be ob0, elsewhere Find the marginal probability density function of YYour answer should contain the region on which the marginal probability density function is nonzero 13 (10 points) Probability and CombinatoricsYou may leave your answer in terms of combinatorics symbols (n

Test Set 6 Probability Density Function Correlation And Dependence
What is joint probability density function
What is joint probability density function-The joint probability density function (joint pdf) of X and Y is a function f(x;y) giving the probability density at (x;y) That is, the probability that (X;Y) is in a small rectangle of width dx and height dy around (x;y) is f(x;y)dxdy y d Prob = f (x;y )dxdy dy dx c x a b A joint probability density function must satisfy two properties 161 Joint density functions Recall that X is continuous if there is a function f(x) (the density) such that P(X ≤ t) = Z t −∞ fX(x)dx We generalize this to two random variables Definition 1 Two random variables X and Y are jointly continuous if there is a function fX,Y (x,y) on R2, called the joint probability density function, such


Http Web Eecs Umich Edu Fessler Course 401 E 94 Fin Pdf
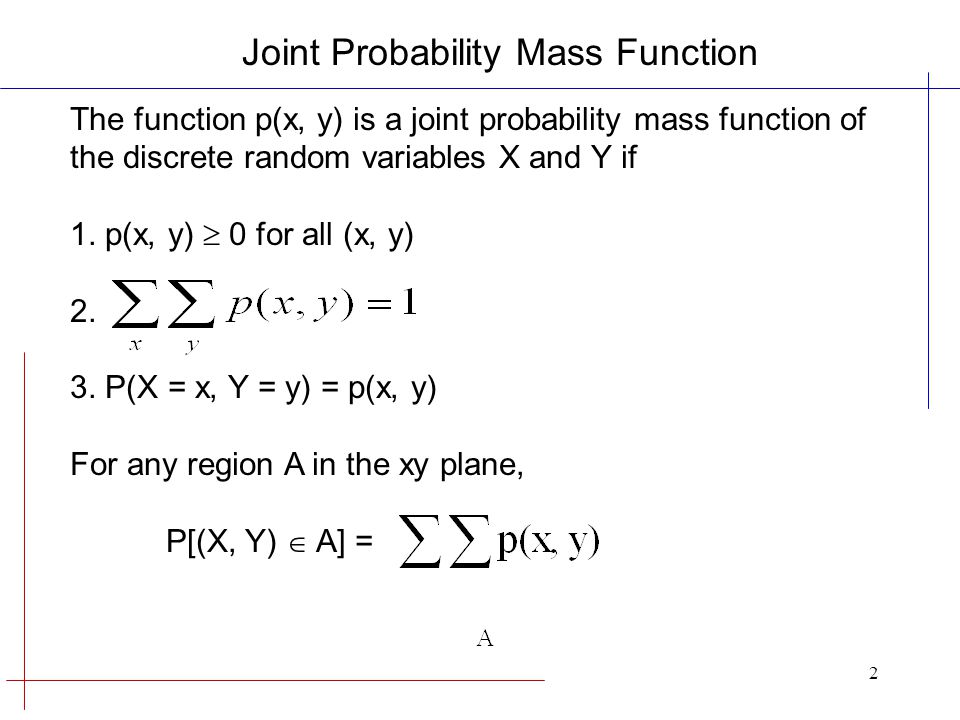
The joint probability distribution can be expressed either in terms of a joint cumulative distribution function or in terms of a joint probability density function (in the case of continuous variables) or joint probability mass function (in the case of discrete variables) These in turn can be used to find two other types of distributions the marginal distribution giving the probabilities forStack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeFor continuous random variables, we have the notion of the joint (probability) density function f X,Y (x,y)∆x∆y ≈ P{x < X ≤ x∆x,y < Y ≤ y ∆y} We can write this in integral form as P{(X,Y) ∈ A} = Z Z A f X,Y (x,y)dydx The basic properties of the joint density function are • f X,Y (x,y) ≥ 0 for all x and y 2
The joint probability density function of the random variables X and Y is {eq}\begin {align*} f\left ( {x,y} \right) &= \dfrac { {3x y}} {9}\;;\;1 < x < 3,\;1 < y < 2\\ & = 0Example 3513 Let X and Y be jointly continuous random variables with joint probability density function f (x, y) = ⇢ 6 e2 x e3 y for 0 < x < 1, 0 < y < 1 0 otherwise Show that X and Y are independent random variables 106How do you compute the P(x>y) for a joint density function in R?
61 Joint density functions Recall that X is continuous if there is a function f(x) (the density) such that P(X ≤ t) = Z t −∞ fX(x)dx We generalize this to two random variables Definition 1 Two random variables X and Y are jointly continuous if there is a function fX,Y (x,y) on R2, called the joint probability density function, suchIf continuous random variables \(X\) and \(Y\) are defined on the same sample space \(S\), then their joint probability density function (joint pdf) is a piecewise continuous function, denoted \(f(x,y)\), that satisfies the followingSimilar to the CDF the probability density function follows the same general rules except in two dimensions, Univariate de nition f (x) 0 for all xf (x) = d dx F(x) R 1 Since the joint density is constant then f(x;y) = c = 2 9;



The Random Variable X And Y Have The Following Joint Probability Mass Function P X Y 23 0 2 Homeworklib
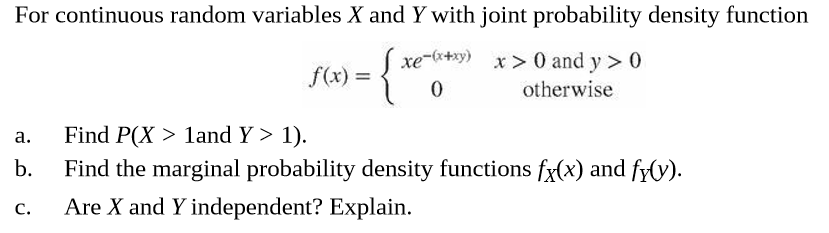


Answered For Continuous Random Variables X And Y Bartleby
0 < y < 2 (a) erifyV that this is indeed a joint density function (b) Compute the density function of X (c) Find P ( X > Y ) (d) Find P ( YExample 3513 Let X and Y be jointly continuous random variables with joint probability density function f (x, y) = ⇢ 6 e2 x e3 y for 0 < x < 1, 0 < y < 1 0 otherwise Show that X and Y are independent random variables 106• Joint probability density function 4 REGRESSION * Line of regression The line of regression of X on Y is given by Example241 1 From the following data, find (i) The two regression equation (ii) The coefficient of correlation between the marks in Economic and Statistics (iii) The
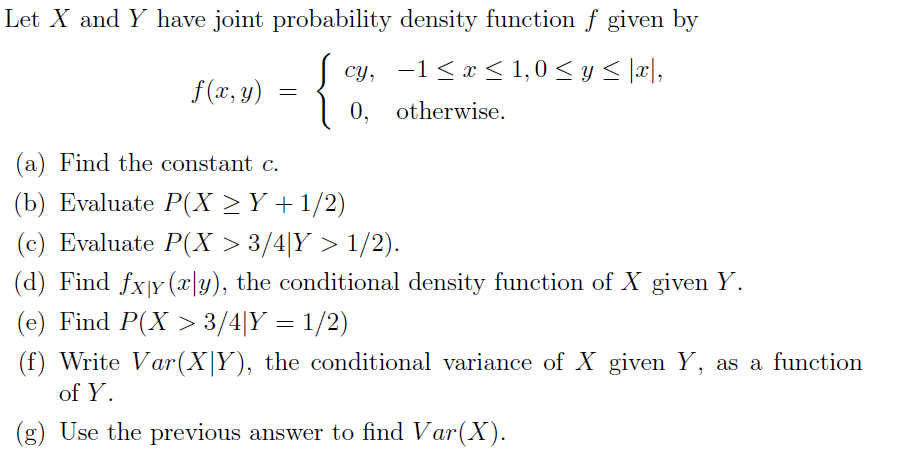


Solved Let X And Y Have Joint Probability Density Functio Chegg Com



The Random Variables X And Y Have Joint Probabilit Chegg Com
The joint probability density function, (,) for two continuous random variables is defined as the derivative of the joint cumulative distribution function (see Eq1) f X , Y ( x , y ) = ∂ 2 F X , Y ( x , y ) ∂ x ∂ y {\displaystyle f_{X,Y}(x,y)={\frac {\partial ^{2}F_{X,Y}(x,y)}{\partial x\partial y}}}If X is a random variable with density fx(x) and Y is a random variable with density fY(y), how would we describe the joint behavior of the tuple (X, Y) at the same time?TheUsing the replicate() function, one simulates this sampling process 1000 times, storing the outcomes in the data frame results with variable names X and YUsing the table() function, one classifies all outcomes with respect to the two variables By dividing the observed counts by the number of simulations, one obtains approximate probabilities similar to the exact probabilities shown in Table 61



Transformations Of A Continuous Random Variable


Http Math Arizona Edu Jwatkins Joint Pdf
The joint probability mass function of (X;Y) is (12) p(xi;yj) = P(X = xi;Y = yj) Example 1 A fair coin is tossed three times independently let X denote the number of heads on the flrst toss and Y denote the total number of heads Find the joint probability mass function of X and Y 2The joint probability density function (joint pdf) of X and Y is a function f(x;y) giving the probability density at (x;y) That is, the probability that (X;Y) is in a small rectangle of width dx and height dy around (x;y) is f(x;y)dxdy y d Prob = f (x;y )dxdy dy dx c x a b A joint probability density function must satisfy two properties 112 (10 points) Let X and Y have joint probability density function defined by f (X,Y) (x, y) = 1 2 x, if 0 < y < x < 2;


Www Stt Msu Edu Users Makagon 351 5 1 Pdf



Poison Distribution Homework Help
For continuous random variables, we have the notion of the joint (probability) density function f X,Y (x,y)∆x∆y ≈ P{x < X ≤ x∆x,y < Y ≤ y ∆y} We can write this in integral form as P{(X,Y) ∈ A} = Z Z A f X,Y (x,y)dydx The basic properties of the joint density function are • f X,Y (x,y) ≥ 0 for all x and y 2As noted in Chapter 1, the joint density function corresponds to the density of points on a scatter plot of x and y in the limit of an infinite number of points This is illustrated in Fig 33, using the data shown on the scatter plot of Fig 13 (b)If X is a random variable with density fx(x) and Y is a random variable with density fY(y), how would we describe the joint behavior of the tuple (X, Y) at the same time?The



1 Suppose That Three Random Variables X Y And Z Have A Continuous Joint Probability Density Homeworklib
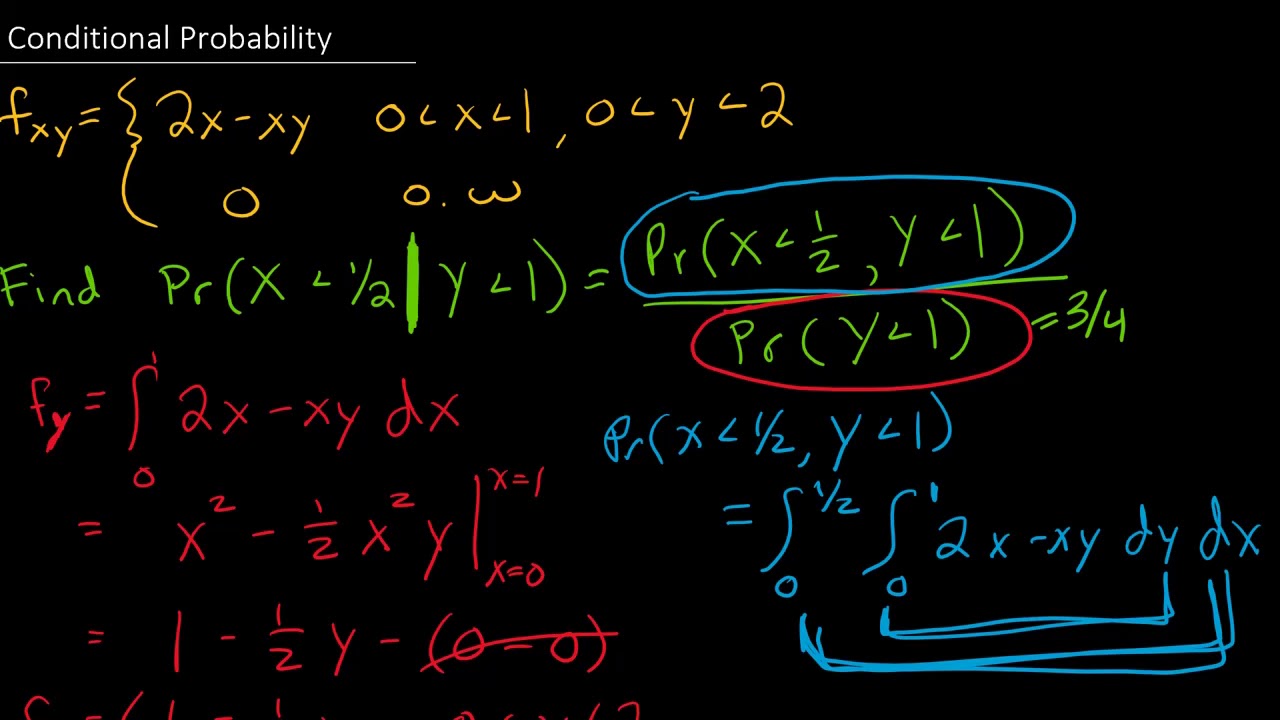


Conditional Probability For X Given Y Is Less Than 1 Provided We Have The Joint Pdf Youtube
Given the following joint probability density function f_xy (x,y) = (6 x y)/8, 0Question Question 2 Let The Joint Probability Density Function For (X,Y) Be F(x,y) = I > 1, Y > 1 For R >1 And Y > 1 Find P(X > 2Y) This problem has been solved!Probability mass function p X(a)=P(X =a)=å y P X;Y(a;y) p Y(b)=P(Y =b)=å x P X;Y(x;b) In the continuous case a joint probability density function tells you the relative probability of any combination of events X =a and Y =y In the discrete case, we can define the function p X;Y nonparametrically Instead of using a formula for p we



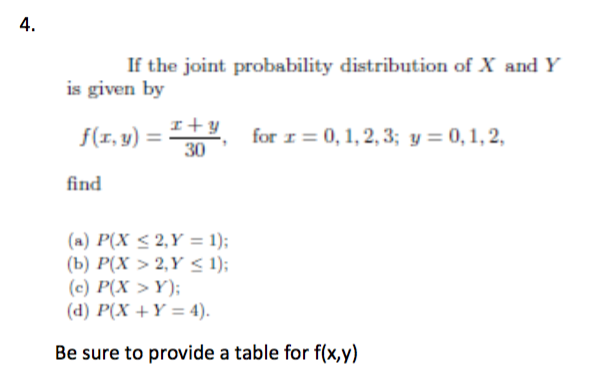
Solved 1 If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Chegg Com



Joint Probability Distribution Wikipedia
Probability Density Function The distribution of a random variable of continuous type is represented by the probability density function (pdf) of the random variableP(X=A) = sum P(X=A, Y=yi) for all y This is another important foundational rule in probability, referred to as the " sum rule " The marginal probability is different from the conditional probability (described next) because it considers the union of all events for the second variable rather than the probability of a single eventThe function f XY(x;y) is called the joint probability density function of Xand Y If nd Bare any sets of real numbers then by letting C= f(x;y) x2 A;y2Bgwe have P(X2A;Y 2B) = Z B Z A f XY(x;y)dxdy In words, to nd the probability that Xand Y take values in any region, we integrate the joint probability density function over that region



Assignment On Random Variables



Product Distribution Wikipedia
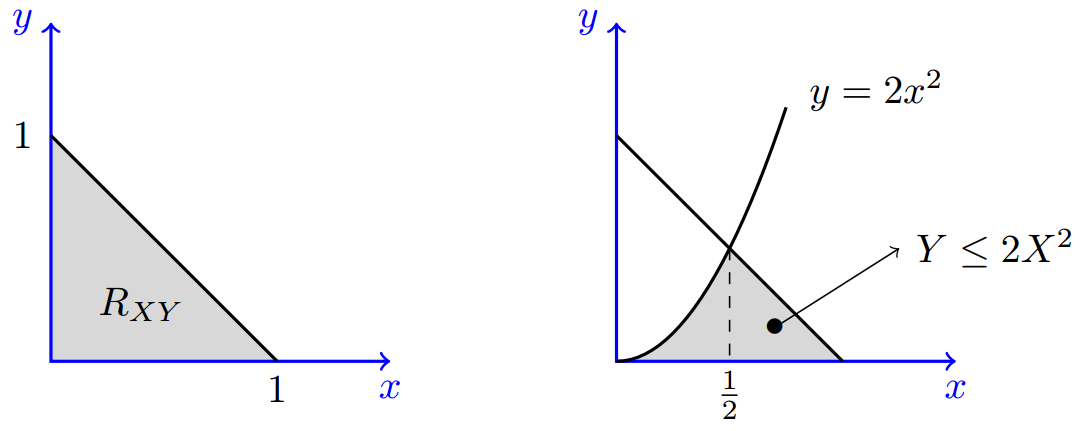
For 0 x y 3 based on the area of the triangle, but we need to be careful to de ne onBivariate Distributions (Joint Probability Distributions) Sometimes certain events can be defined by the interaction of two measurements These types of events that are explained by the interaction of the two variables constitute what we call bivariate distributions When put simply, bivariate distribution means the probability that a certain event will occur when there are two independentUsing the replicate() function, one simulates this sampling process 1000 times, storing the outcomes in the data frame results with variable names X and YUsing the table() function, one classifies all outcomes with respect to the two variables By dividing the observed counts by the number of simulations, one obtains approximate probabilities similar to the exact probabilities shown in Table 61


2


Http Www Sfu Ca Baa7 Teaching 02 Joint Distributions
See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Previous question Next question Transcribed Image Text from this Question• Joint probability density function 4 REGRESSION * Line of regression The line of regression of X on Y is given by Example241 1 From the following data, find (i) The two regression equation (ii) The coefficient of correlation between the marks in Economic and Statistics (iii) TheFZ(z) = P(Z ≤ z) = P(X Y ≤ z) = P(Y ≤ −X z) = ˆ0 if z < 0 Rz 0 Rz−x 0 λe −λxλe−λydydx = 1−e−λz −λze−λz if z ≥ 0 This gives the pdf, fZ(z) = ˆ 0 if z < 0 λ2ze−λz if z ≥ 0, which is the pdf of a Gamma(2,λ) Thus, Z is Gamma(2,λ) random variable (b)



Two Random Varibales X And Y Have A Joint Probability Density Function Of The Form F X Y K X 2y 0 Two Random Varibales X And Y Have A Joint Probability Density Function Of



2 Two Random Variables X And Y Have The Joint Pdf A Find Fyix Yx And Verify Homeworklib
P(X=A) = sum P(X=A, Y=yi) for all y This is another important foundational rule in probability, referred to as the " sum rule " The marginal probability is different from the conditional probability (described next) because it considers the union of all events for the second variable rather than the probability of a single eventFxx(x, y) = { % 0, otherwise Note e' = Find the P(X < 13 n Y < 14)The joint probability mass function of two discrete random variables $X$ and $Y$ is defined as \begin{align}%\label{} \nonumber P_{XY}(x,y)=P(X=x, Y=y) \end{align}


2



Q3 Suppose That Joint Probability Function Of X And Y Is Given By 1 7 Homeworklib
Ask Question Asked 2 years, 5 months ago Active 2 years, 5 months ago Deriving the joint probability density function from a given marginal density function and conditional density function 2 Conditional Probability Mixture Model 5If continuous random variables X and Y are defined on the same sample space S, then their joint probability density function ( joint pdf) is a piecewise continuous function, denoted f ( x, y), that satisfies the following f ( x, y) ≥ 0, for all ( x, y) ∈ R 2 ∬ R 2 f ( x, y) d x d y = 1 P ( ( X, Y) ∈ A) = ∬ A f ( x, y) d x d y, for any A ⊆ R 2 The first two conditions in Definition 521 provide the requirements for a function to be a valid joint pdfXY (xy) satisfies the properties of an ordinary (onevariable) density function;


Solved Suppose Random Variables X And Y Have Joint Probability Density Function F X Y 63 Quot 3 23 For 0 Lt X Lt Y Lt 00 0 Otherwise Course Hero


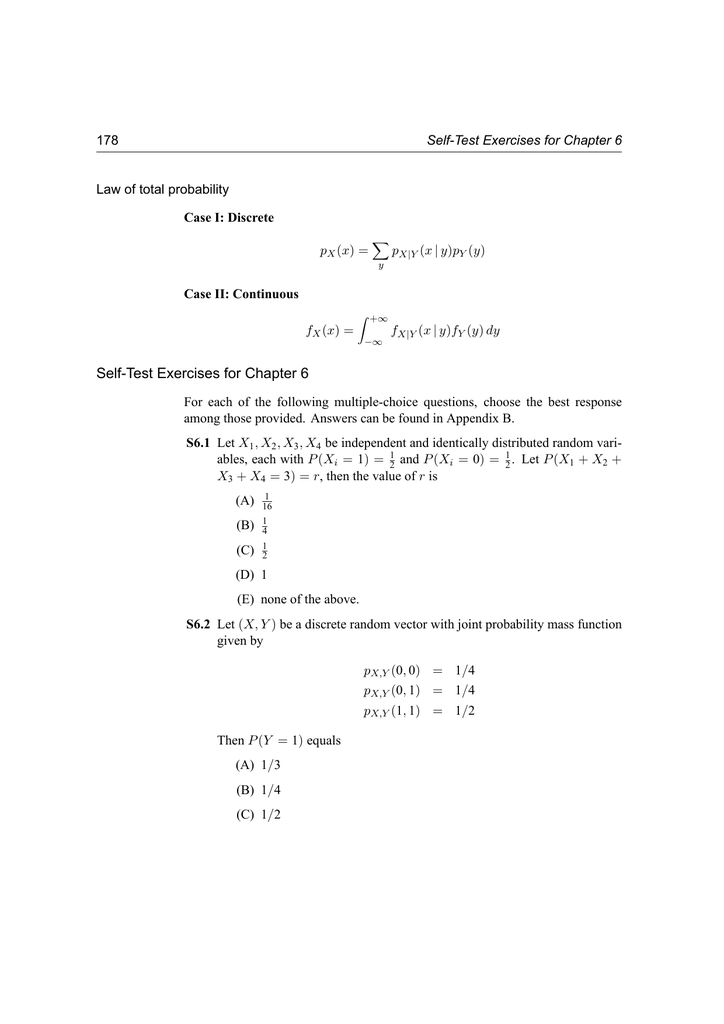
Faculty Math Illinois Edu Hildebr 370 Problemsets Problemset4s Pdf
The same goes for f Y X(yx) • Probabilities via joint densities Given a region B in the xyplane, the probability that (X,Y) falls into this region is given by the double integral of f(x,y) over this region P((X,Y) ∈ B) = ZZ B f(x,y)dxdy0, elsewhere Find the marginal probability density function of YYour answer should contain the region on which the marginal probability density function is nonzero 13 (10 points) Probability and CombinatoricsYou may leave your answer in terms of combinatorics symbols (n0 < x < 1 ;
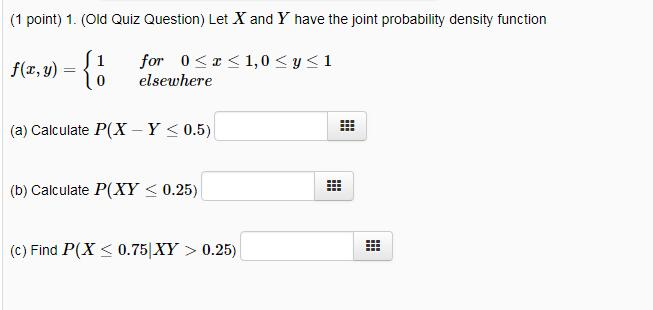


Solved 1 Point 1 Old Quiz Question Let X And Y Have Chegg Com


Http Web Eecs Umich Edu Fessler Course 401 E 94 Fin Pdf
P(X=A) = sum P(X=A, Y=yi) for all y This is another important foundational rule in probability, referred to as the " sum rule " The marginal probability is different from the conditional probability (described next) because it considers the union of all events for the second variable rather than the probability of a single eventStack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeThe joint probability mass function of two discrete random variables $X$ and $Y$ is defined as \begin{align}%\label{} \nonumber P_{XY}(x,y)=P(X=x, Y=y) \end{align}


Http Www Stat Osu Edu Mb Chap5 427 Pdf
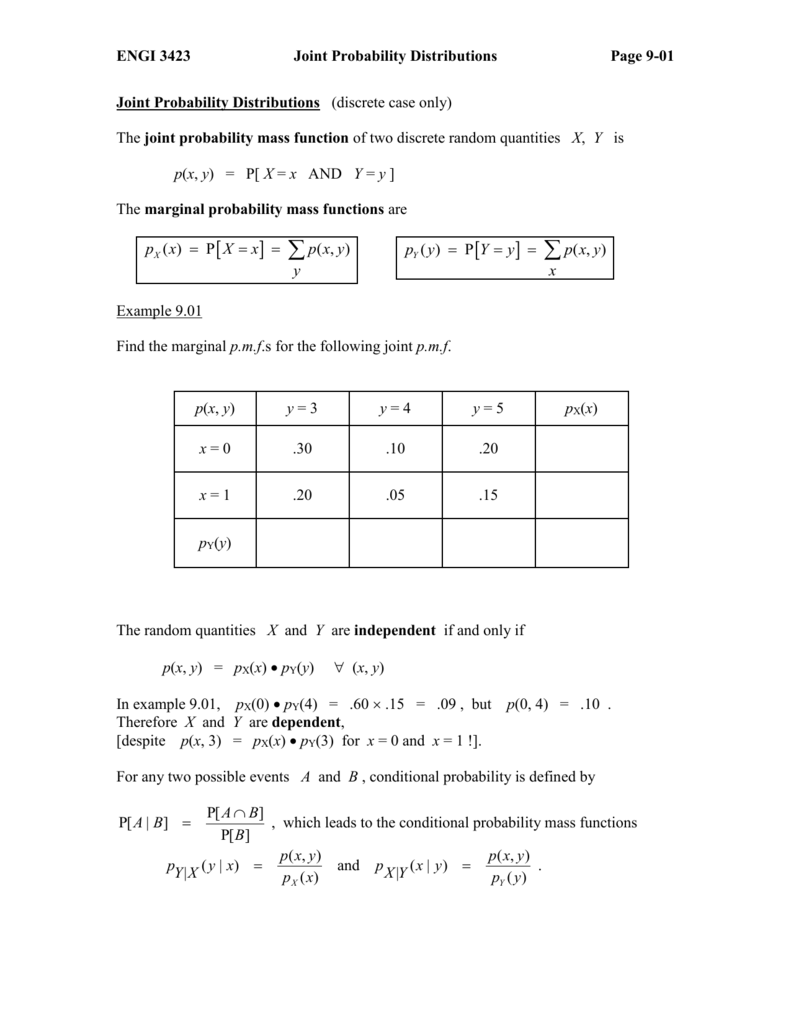


Joint Probability Distributions
Joint Probability Density Function A joint probability density function for the continuous random variable X and Y, denoted as fXY(x;y), satis es the following properties 1 fXY(x;y) 0 for all x, y 2 R 1 1 R 1 1 fXY(x;y) dxdy= 1 3 For any region Rof 2D space P((X;Y) 2R) = Z Z R fXY(x;y) dxdy For when the rv's are continuous 16P ( ( X, Y) ∈ A) = ∬ A f X Y ( x, y) d x d y ( 515) The function f X Y ( x, y) is called the joint probability density function (PDF) of X and Y In the above definition, the domain of f X Y ( x, y) is the entire R 2 We may define the range of ( X, Y) as R X Y = { ( x, y) f X, Y ( x, y) > 0 }The probability that the ordered pairs of random variables (X, Y) (X,Y) (X, Y) take values in the (open or closed) intervals a, b a,b a, b and c, d, c,d, c, d, respectively, is given by the integral of a function called the joint probability density function f X Y (x, y) f_{XY} (x,y) f X Y (x, y)
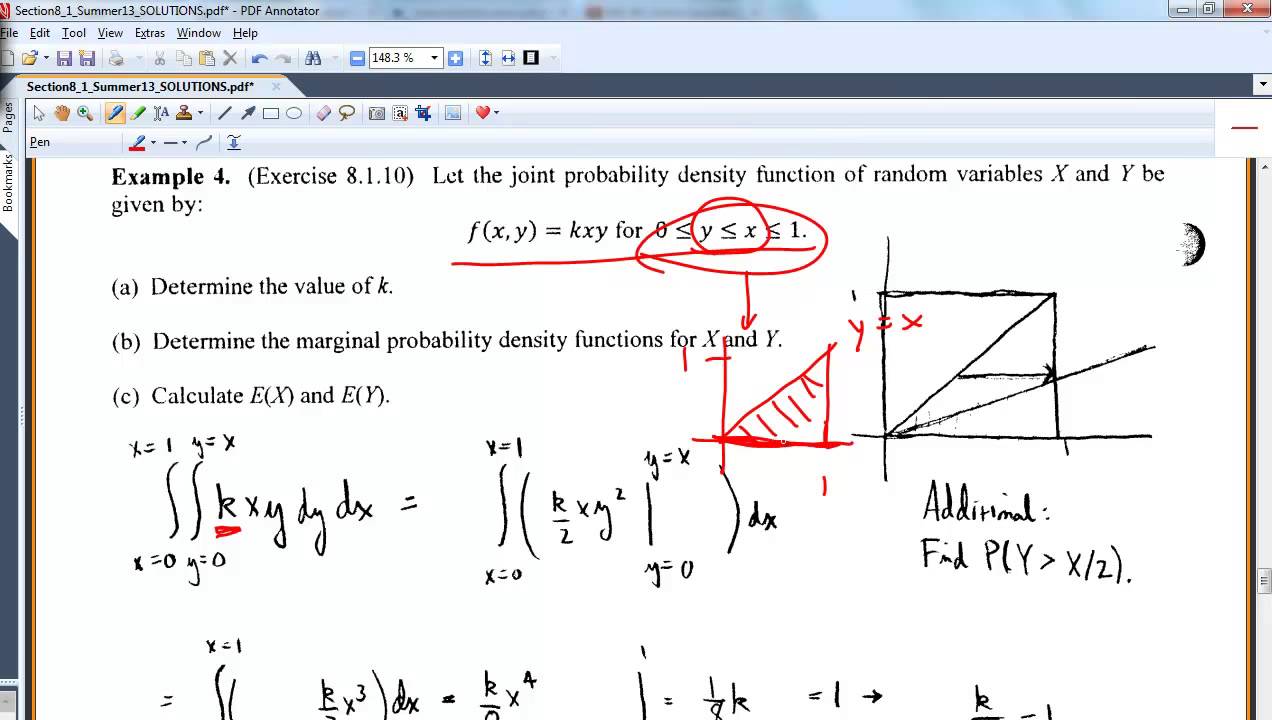


Ma 381 Section 8 1 Joint Probability Density Functions Youtube



2 Let The Random Variables X And Y Have The Joint Pdf Given Below A Find P X Y 2 B Find The Marginal Pdfs O Homeworklib
Example 3513 Let X and Y be jointly continuous random variables with joint probability density function f (x, y) = ⇢ 6 e2 x e3 y for 0 < x < 1, 0 < y < 1 0 otherwise Show that X and Y are independent random variables 106The function p defined for all (x i, y j) in the range space (X, Y) is called the probability function of (X, Y) The set of triplets (x i, y j;p(x i, y j)) i, j = 1, 2, is called the probability distribution of (X, Y) Joint Density Function Let (X, Y) be a continuous random variable assuming all values in some region R of the Euclidian planeIn the joint density Obtaining this probability is called marginalization, and it involves taking a weighted sum2 over the possible outcomes of the rv's that are not of interest For two variables X,Y P(X = x) = X y P(x,y) = X y P(X = xY = y)P(y) In this case P(X) is often called a marginal probability and the process of



2 The Joint Probability Density Function Of X And Chegg Com


Pradeepchandrasekar Weebly Com Uploads 4 7 8 2 Unit 2 03 Pdf
1 Let p(x,y) be the uniform joint probability density on the unit disk, ie, and p(x,y)=0 otherwise Calculate the pdf of XY Also find the expected value and variance of XY 2 Suppose X and Y are independent random variables, each distributed according to the exponential distribution with parameter Find the joint pdf of X and Y (easy)Cross Validated is a question and answer site for people interested in statistics, machine learning, data analysis, data mining, and data visualization= 10 ways Hence the probability P ( N 1 = i;N 2 = j ) = 1 10 1 i < j < 5 Q 3) (Ross # 69) The joint probability density function of X and Y is given by f ( x;y ) = 6 7 x 2 xy 2 ;



The Joint Probability Density Function Of X And Y Is Given By F X Y 67 X2 Xy2 0 Hwmadeeasy
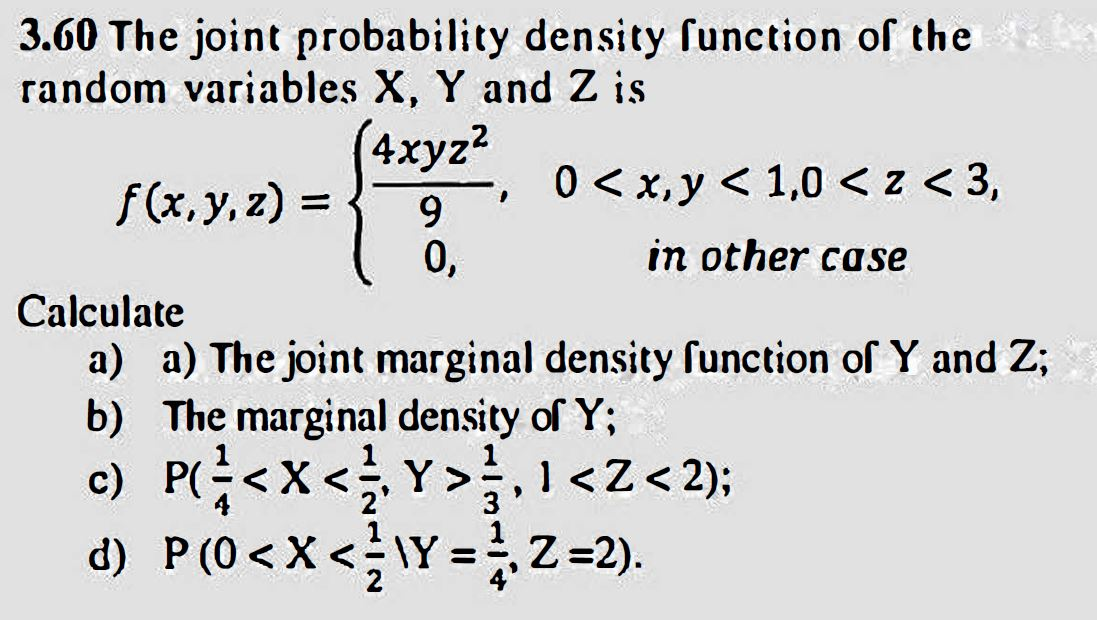


Solved 3 60 The Joint Probability Density Function Of The Chegg Com
The joint probability density function of two random variables X and Y is given by 2y 0 < x < 2,0 < y;
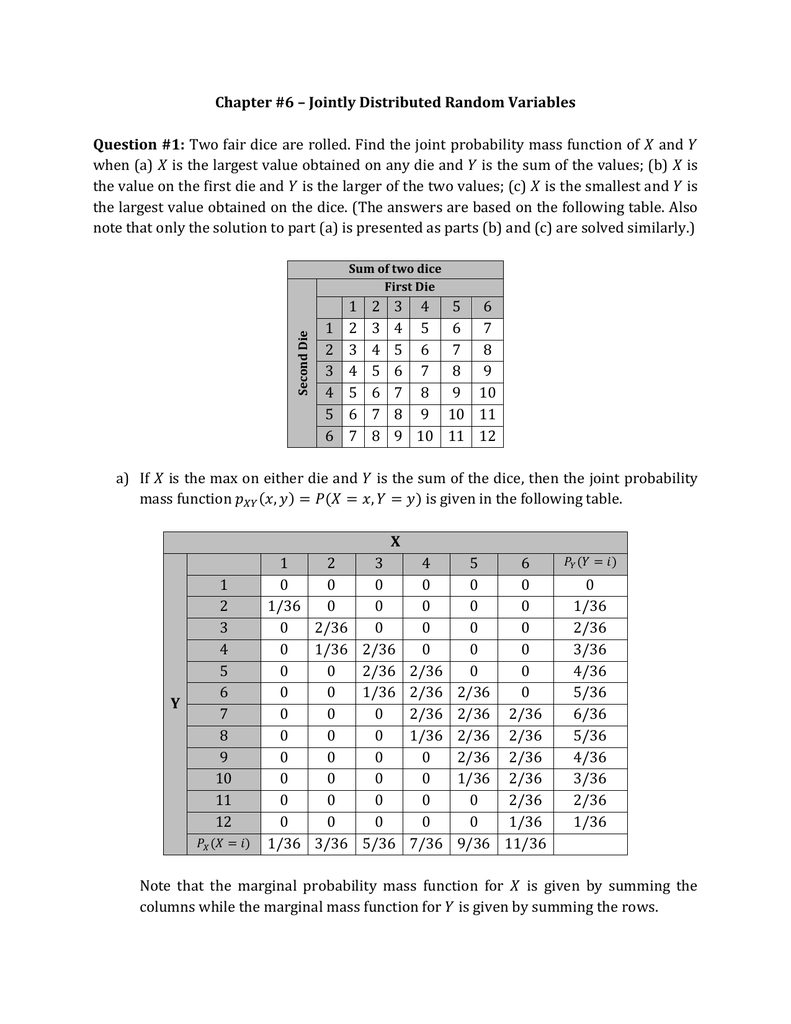


Chapter 6 Jointly Distributed Random Variables Question 1


Http Faculty Atu Edu Mfinan 3153 Section26 Pdf


Www Pnw Edu Wp Content Uploads 03 Lecturenotes6 10 Pdf


Solved 1 The Joint Probability Density Function Pdf Of Chegg Com


How To Do A Joint Probability Density Function Of F X Y Youtube



Joint Probability Distribution Wikipedia



Test Set 6 Probability Density Function Correlation And Dependence


Lesson 17 Distributions Of Two Discrete Random Variables


Solved 4 Random Variables X And Y Have Joint Probability Chegg Com



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides


Chapter6 Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download



Joint Probability Distributions And Random Samples Whelan Courses 10 4wi 1016 345 Probability Distributions Pdf Document



Unit Ii Rpq



Chapter 4 Joint And Conditional Distributions Ppt Download



Unit Ii Rpq


Joint Probability Distributions



Problems And Solutions 4



Answered 5 Let X And Y Be Random Variables Bartleby



St 371 Viii Theory Of Joint Distributions Pdf Free Download


Joint Cumulative Distributive Function Marginal Pmf Cdf



Home Work Shortcuts 3 13 Two Random Variables X And Y Have The Joint Distribution P 0 0 0 2 P 0 2 0 3 P 1 1 0 1 P 2 0 0 3 P 2 2


Http Isa Site Nthu Edu Tw App Index Php Action Downloadfile File Wvhsmflxtm9mekkytdncmflwohppre0wtvy4mu5urxdnrekwwhpjnu56ttnmbkjrwmc9pq Fname 0054rob0rksscd11ggxsnkxtdctwcglkwsfggcnk41jdoocckp30cdsw3454swuslowwttihdgpoegch34kob4npfgmojdhcccvxxwfc34b4wxklooporpfcss40ssxt


Www Utdallas Edu Efrom Solhw Pdf


Conf Math Illinois Edu Rsong 461f10 Lect6 Pdf


Q Tbn And9gcrwhzokremzetz Tgkypcv94zovgjvr2lzwuhvm Vzrww1fto Usqp Cau


Solved If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y I Chegg Com


Solved Problems Pdf Jointly Continuous Random Variables



Statistical Sciences 2141a B Lecture Notes Fall 18 Lecture 14 Probability Density Function Probability Mass Function Joint Probability Distribution


Http Home Ku Edu Tr Mmuradoglu Engr1 Engr1hw5sol Pdf


Http Homepage Divms Uiowa Edu Rdecook Stat Notes Ch5 Pt2 Pdf



Intuition Of Joint Density Of Min X Y And Max X Y Mathematics Stack Exchange



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides


Http Homepage Stat Uiowa Edu Rdecook Stat Hw Hw7 Pdf
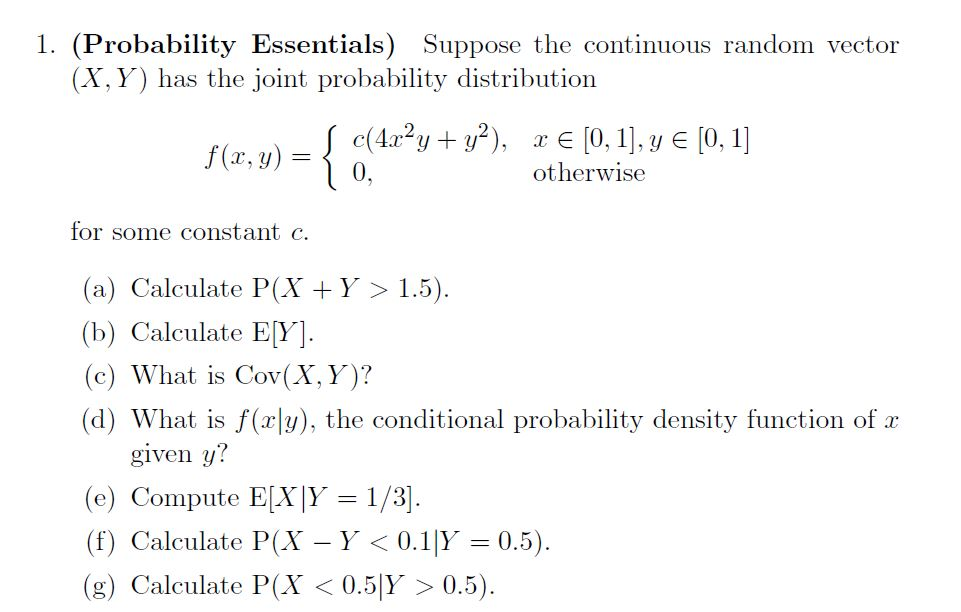


Suppose The Continuous Random Vector X Y Has Th Chegg Com


Http Homepage Stat Uiowa Edu Rdecook Stat Notes Ch5 Pt1 Pdf



Marginal Pdf From Joint Pdf Youtube



Solved Let The Joint Probability Density Function For X Chegg Com


Joint Probability Distributions Leadership In Engineering Ppt Video Online Download


Joint Probability Density Function Joint Continuity Pdf



Newbold Chapter 4 Part2 Stat 210 0 Studocu


3 4 Joint Probability Distributions Ppt Video Online Download


Faculty Math Illinois Edu Hildebr 370 370jointdistributions Pdf


Search Q Joint Probability Formula Tbm Isch


Self Test Exercises For Chapter 6



St 371 Viii Theory Of Joint Distributions Pdf Free Download



Chapter 5 Joint Probability Distributions Part 1 Sections 5
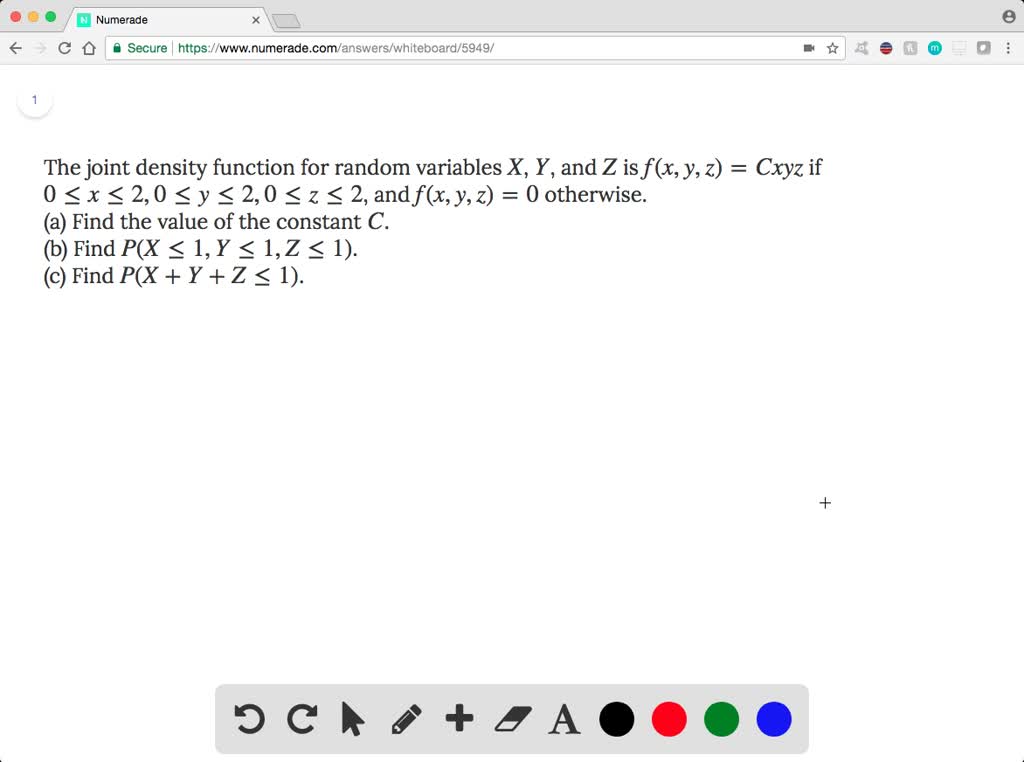


Solved The Joint Density Function For Random Vari


Http Home Ku Edu Tr Mmuradoglu Engr1 Engr1hw5sol Pdf



How To Find The Mean And Variance Of Minimum Of Two Dependent Random Variables



Solved The Joint Probability Density Function Of X And Y Chegg Com



Solved Let The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y Chegg Com


3
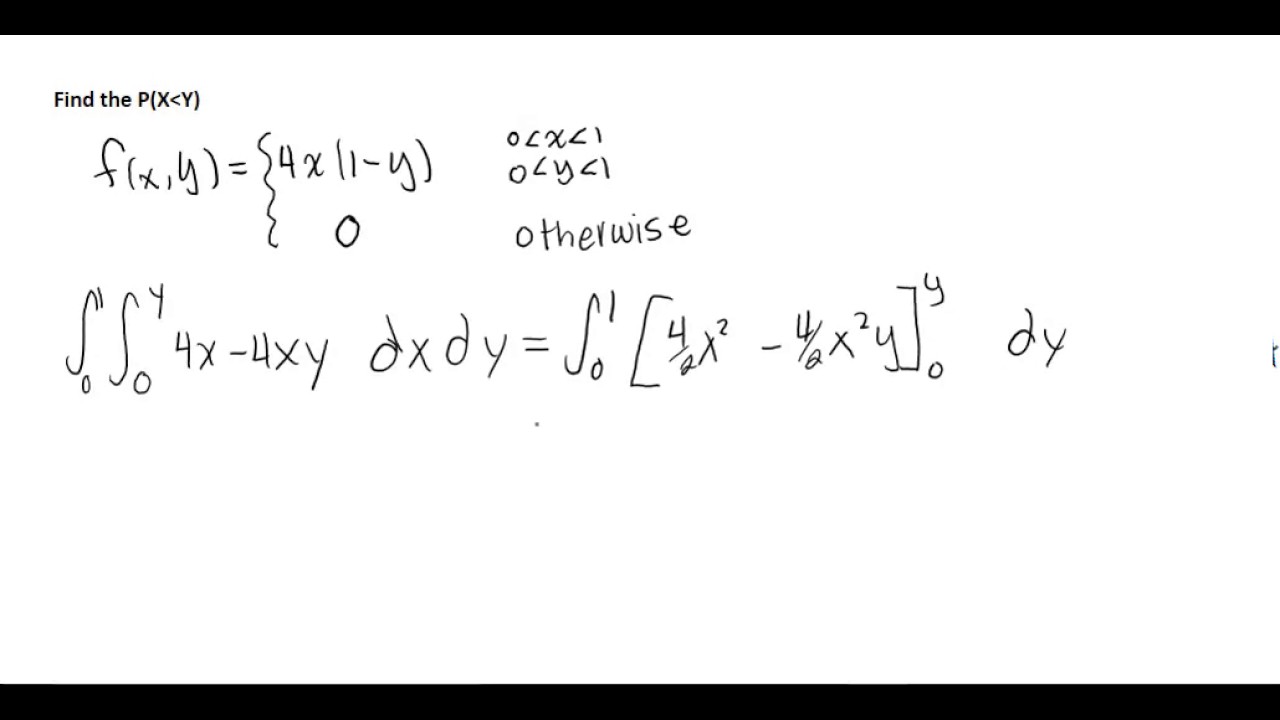


P X Less Than Y From Joint Pdf Youtube
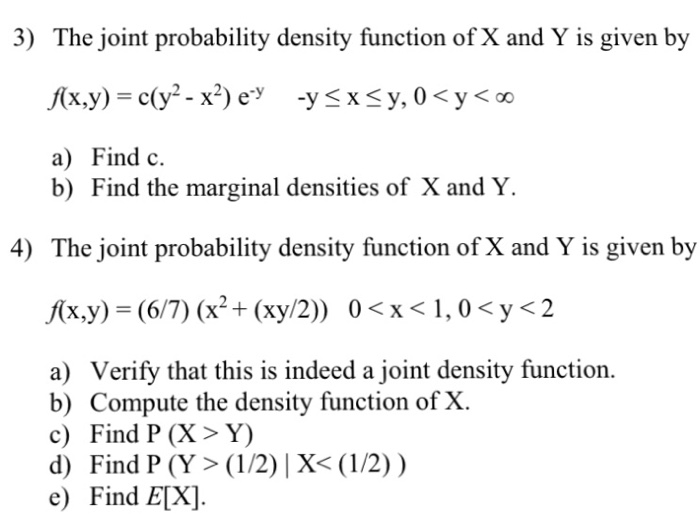


Solved The Joint Probability Density Function Of X And Y Chegg Com



Mth4106 Introduction To Statistics



Find P X Y Le 0 Given The Joint Probability Function Of X And Y Mathematics Stack Exchange
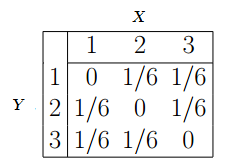


Joint Probability And Joint Distributions Definition Examples Statistics How To



Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download


Joint Probability Distribution


Suppose That X And Y Are Random Variables With Joint Probability Density Function F X Y 6xy 0 Lt X Lt Y Lt 1 0 Otherwise A Find The Marginal Course Hero


Www Math Uh Edu Bekki 3339 Notes 3339day11done Pdf
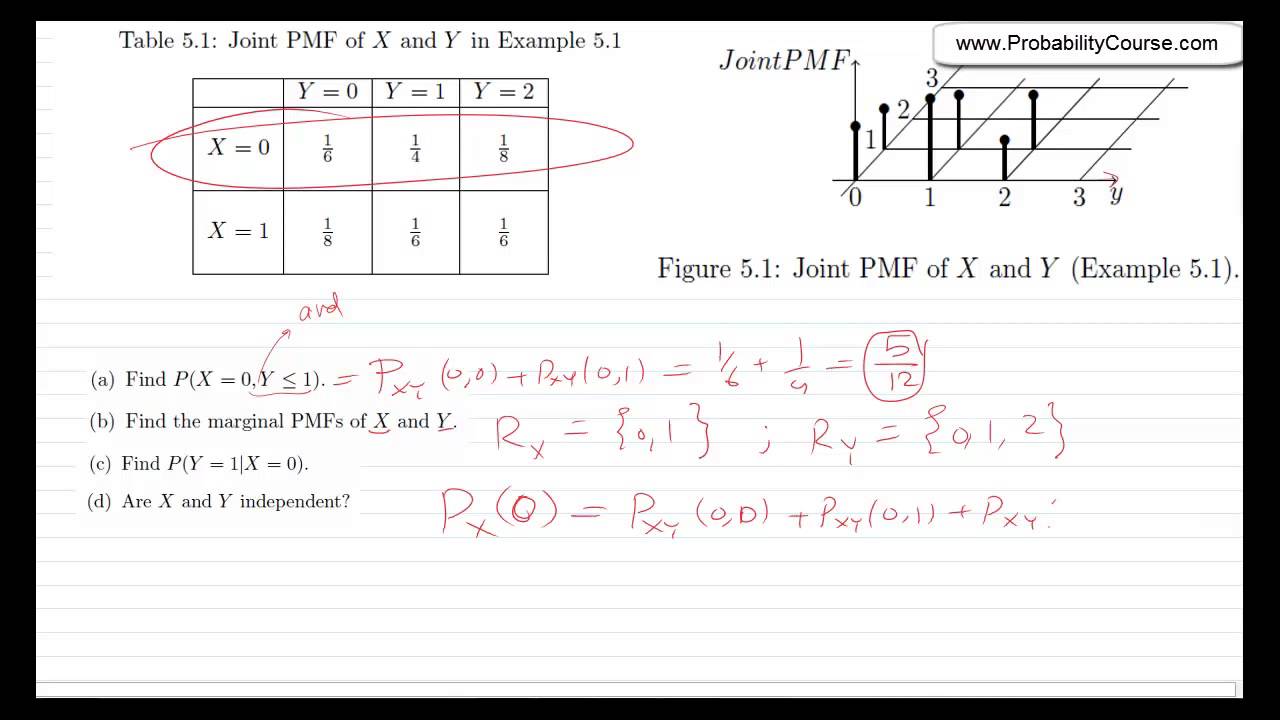


38 Joint Probability Mass Function Pmf Youtube



Answered Section 2 6 Given The Joint Bartleby


Joint Probability Distributions



Poison Distribution Homework Help
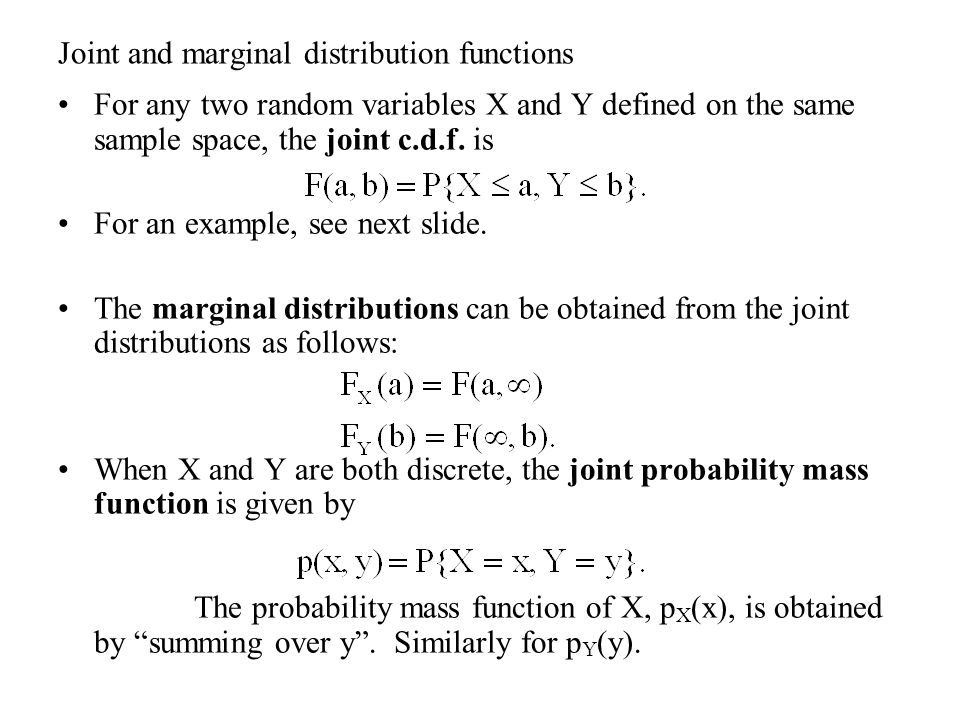


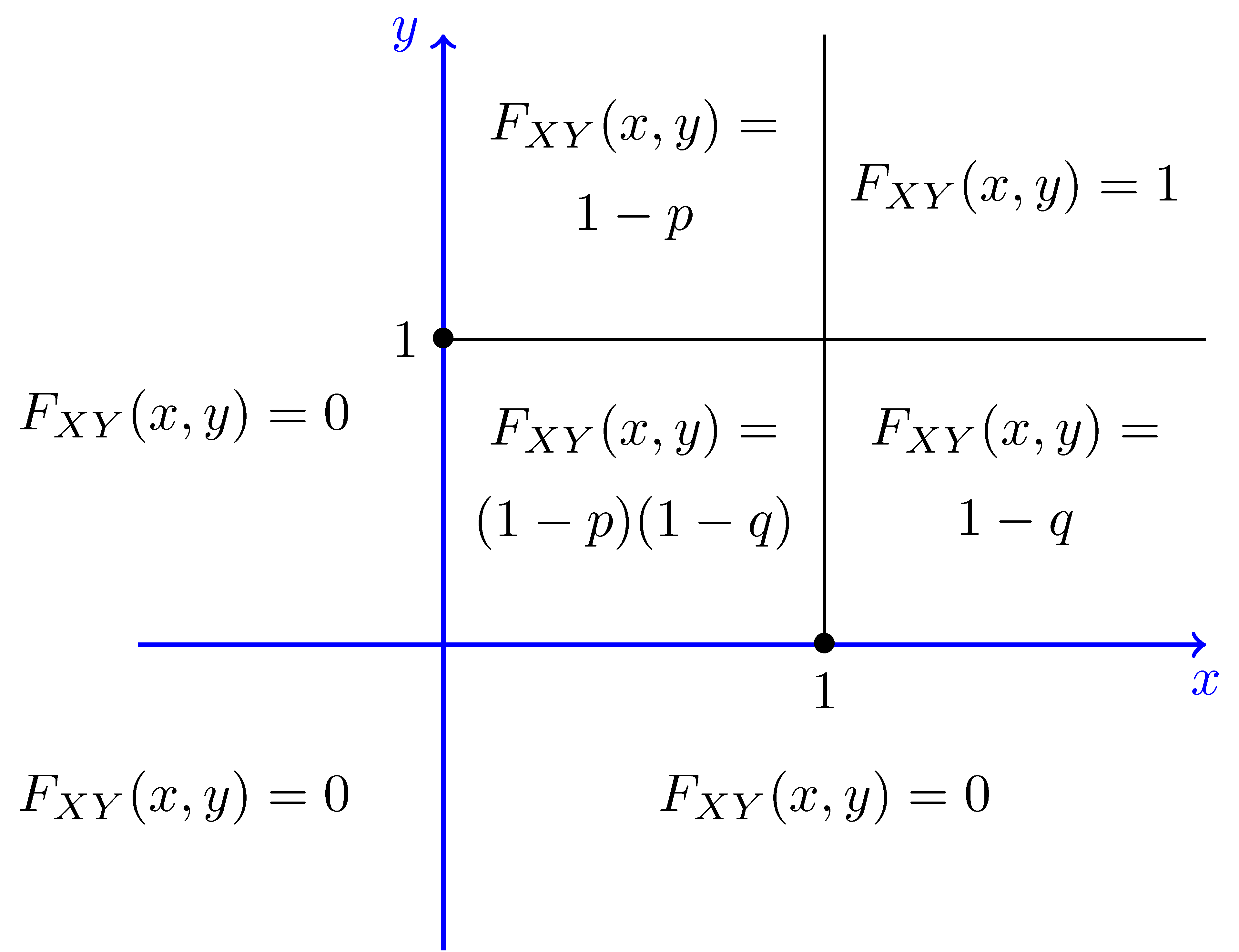
Joint And Marginal Distribution Functions For Any Two Random Variables X And Y Defined On The Same Sample Space The Joint C D F Is For An Example See Ppt Download



Pdf Section 6 1 Joint Distribution Functions


Www Bauer Uh Edu Rsusmel Phd Sr 6 Pdf


Http Www2 Latech Edu arron Chapter5 Pdf



Solved 139 Probability Calculations Let The Joint Probab Chegg Com


2


コメント
コメントを投稿